
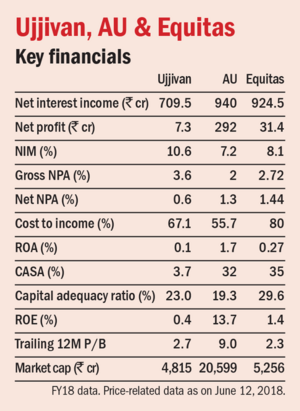
Small-finance banks are niche banks with the prime motive of financial inclusion. They have to lend to small business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries and unorganised-sector entities, whereas other banks can provide loans to all sections of society. There are three such banks listed on the stock exchanges: Ujjivan, AU Small Finance Bank and Equitas.
 Payments banks are also differentiated banks like small-finance banks, with the prime motive of financial inclusion. They aim to reach the remotest parts of India through mobile phones, which is economical as compared to expensive traditional branch networks. Their main role is to facilitate payments and remittances
Payments banks are also differentiated banks like small-finance banks, with the prime motive of financial inclusion. They aim to reach the remotest parts of India through mobile phones, which is economical as compared to expensive traditional branch networks. Their main role is to facilitate payments and remittances
There are many payment banks in the country but none of them has a direct presence on the stock market. However, the three major telecom companies - Airtel, Reliance Jio and Idea Cellular have their own payment banks.
The business models
Small-finance banks have to abide by the following rules:
1. They have to maintain a capital-adequacy ratio of 15 per cent in comparison to 12 per cent mandated for other banks.
2. They have a minimum capital requirement of Rs100 crore versus Rs500 crore for commercial banks.
3. More than 50 per cent of their loans should be less than Rs25 lakh. There is no such restriction for commercial banks.
4. They have to lend 75 per cent of their lendable capital to the priority sector in comparison to 40 per cent for commercial banks.
Here is what differentiates payment banks from traditional banks:
1. They can accept deposits but only up to Rs1 lakh.
2. They cannot lend. They are mandated by the RBI to keep 75 per cent of deposits in government securities and remaining 25 per cent with commercial banks.
3. They cannot issue credit cards but can issue ATM/debit cards.
Payment banks earn from following activities:
1. The differential between what they pay on deposits and what they earn on their deposits with the RBI and other banks. But this is not a high-margin source since they have to pay a higher rate of interest than other traditional banks to attract customers.
2. They can charge their customers for cash withdrawals.
3. They also earn some commission by selling third-party financial products like insurance and mutual funds.
4. They also enable bill payments, mobile recharges, e-commerce payments and other transactions.
This article is part of a series on how to assess new business models.
