
Equity and debt are two primary asset classes. While equity is volatile and holds high growth potential, debt tends to be steadier and offers predictability. Arriving at an appropriate asset allocation is about deciding the optimum mix of equity and debt in your portfolio.
Unlike the stock market, the current structure of the Indian bond market makes it very difficult for Indian retail investors to buy/sell bonds directly. Thus, several investors resort to debt funds for adding bonds to their portfolios. Another cost-effective way of adding bonds to one's portfolio is debt ETFs (exchange-traded funds).
Like equity ETFs comprise stocks of the underlying index, debt ETFs are passive investment instruments that invest in fixed-income securities in the same proportion as the underlying index. Being an ETF, they are traded on the stock exchange.
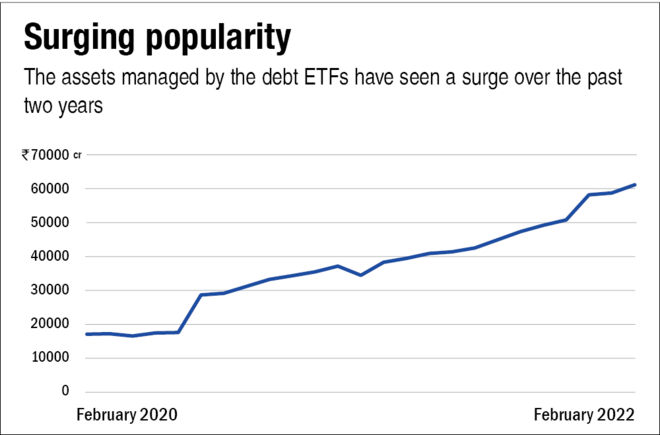
The Indian mutual fund industry currently hosts 16 debt ETFs across categories such as liquid, medium-duration, medium to long duration, long-duration, gilt, and gilt with 10-year constant duration. While the first debt ETF was launched in 2003, it was only after late 2019, that these funds saw a surge in popularity. The assets managed by these ETFs have grown at an annual rate of over 91 per cent in the past two years from over Rs 16,500 crore (as on February 29, 2020) to over Rs 60,400 crore (as on February 28, 2022). Long-duration debt ETFs manage largest assets currently.
While the majority of investments made in debt ETFs are by institutional investors, these have started becoming popular with retail investors due to the several advantages they offer.

Why invest in debt ETFs
- Low-cost: Since debt ETFs aim to simply replicate the underlying index, they are a cost-effective method of investing in debt securities compared to their actively managed counterparts. For instance, as against the median expense ratio of 0.83 per cent for actively managed long-duration debt funds (direct plan), the ETFs in this space cost only 0.001 per cent.
- Liquidity: Debt ETFs are convenient to buy and sell and hence provide ease of trading. Authorised participants (APs), also known as the market makers, purchase or sell units on the exchange based on the supply and demand and hence ensure that the ETF trades at a price close to its fair value.
- Transparency: When you invest in an ETF, you know well in advance what securities you would be exposed to. Moreover, the portfolio of debt ETFs is disclosed on a daily basis. Also, as debt ETFs trade on an exchange, they provide real-time prices to investors.
Disclaimer: Mutual fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme related documents carefully.
All Mutual Fund investors have to go through a one-time KYC (Know Your Customer) process. Investors should deal only with Registered Mutual Funds (RMF).
For further information on KYC, RMFs and procedure to lodge a complaint in case of any grievance, you may refer the Knowledge Center section available on the website of Mirae Asset Mutual Fund.








