
One of our readers recently wrote to us asking how they can check the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of a mutual fund scheme on our Value Research Online website. And more importantly, if the same can be checked for a historical period.
One can check the latest P/E ratio of a fund on Value Research Online, by clicking on the 'Portfolio' tab of the fund page. Look for the box with the heading - 'Concentration & Valuation'. Besides the P/E ratio, you would also get to know the latest price-to-book (P/B) ratio of the fund.
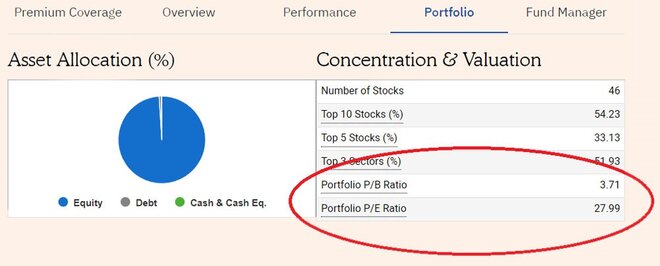
However, it isn't possible to access the historical P/E and P/B ratios for a fund on our website. But are they so important? Well, that's another question that we are often asked - how important or relevant is the P/E ratio when choosing an equity mutual fund scheme? To answer this, let us first understand what the P/E ratio is.
For a company, a P/E ratio tells you how much investors are willing to pay for one rupee of its earnings (profits). It is the ratio of the share price of a company to its earnings-per-share (EPS). EPS is the profit that a company makes on a per share basis. So, if EPS is one, the P/E ratio will reflect the price that an investor will pay for this one rupee of the company's profits. Because of this relation with a company's profits, this ratio is also called the earnings multiple.
Some shares have a higher P/E ratio and some lower. A higher P/E ratio signifies that investor expectation from these shares is higher. This is because the growth in share price is expected to follow earnings growth. So, if investors are willing to pay more for a share, it is because they are expecting faster growth in profits. These stocks are often referred to as growth stocks.
At the other end are companies that have a low earnings multiple. Here, investors are not expecting much growth, and these stocks are called value stocks. The situation could change as a company that has been growing slowly can gather pace and a fast-mover can slow down. Growth and value are thus not static concepts.
What about funds? Well, first of all, an equity fund is a collection of shares. Therefore, a fund's P/E is the average of the P/Es of all stocks, in proportion to their presence in the portfolio. Because fund portfolios change, the P/E will also change and this will not reflect the growth prospects of the underlying assets. A fund's PE is the weighted average PE of its stocks. Cash has no role to play. Thus, caution has to be exercised and the cash component has also to be factored in while looking at P/Es. Similarly, loss-making companies are assigned a zero value. For these reasons, a fund's P/E is not as relevant as that of a share.
Nonetheless, a fund's P/E can be used for comparing funds in its category, or in comparing categories. It gives you a rough sense of whether a fund is value-oriented or high-growth-oriented. However, it is only a rough guide to the relative valuation and nothing more and it should not play a critical part for you to make a judgment based on this alone.
In the beginning, the focus should be on identifying funds and fund managers that have a track record of doing consistently well through multiple market cycles. So, one should look for funds that have done consistently well through the ups and downs of the market and avoided big disasters. Once one has been able to zero in on a narrow list of such funds, then one may refer to these valuation ratios of a fund like a P/E ratio to bring some style diversity in their selection of funds which they want to eventually add to their portfolio.
Suggested watch:
Are P/E and P/B ratios relevant when it comes to selecting a mutual fund scheme?
What is the preferred P/E range when investing in an index fund?








